목차
토글분해성 폴리머 마스터배치 압출 및 펠렛화 장비란 무엇입니까?
분해성 폴리머 마스터배치 압출 및 펠렛화 장비 분해성 첨가제와 폴리머를 농축한 혼합물인 분해성 폴리머 마스터배치를 생산하는 데 사용되는 특수 기계를 말합니다.
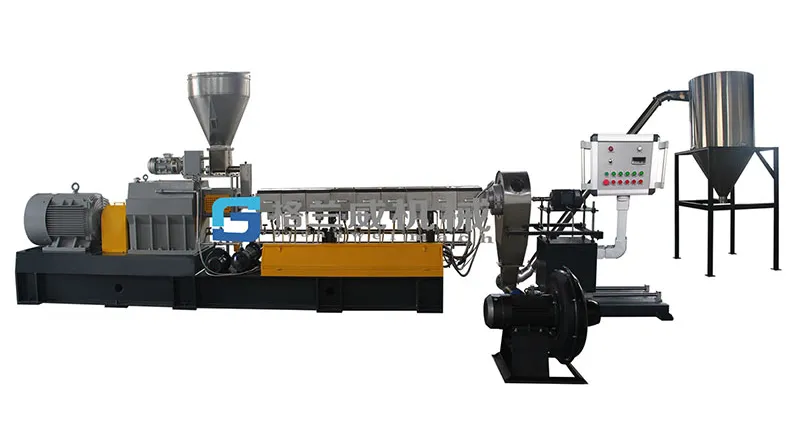

분해성 마스터배치란 무엇인가요?
분해성 마스터배치는 제조 중에 특정 환경 조건에서 분해를 가속화하기 위해 생분해성 첨가제의 농축 혼합물의 작은 과립을 말합니다. 비용을 줄이기 위해 이 마스터배치 공식에서 일정 비율의 CaCO3, 옥수수 전분 및 기타 무기 물질을 가열합니다. 동시에 옥수수 전분과 CaCO3의 특성으로 인해 플라스틱 제품의 분해를 가속화합니다. 첨가량은 최종 제품에 따라 15-60%로 다릅니다.
분해성 마스터배치의 종류
생분해성 마스터배치:
플라스틱의 생분해성을 높여 미생물이 물, 이산화탄소, 바이오매스와 같은 천연 물질로 분해할 수 있도록 합니다.
생분해성 마스터배치의 주요 구성 요소는 다음과 같습니다.
- 기본 폴리머: PE, PP, PS.
- 광분해성 첨가제: 자외선 흡수제, 광산화제, 금속 스테아레이트.
- 블렌딩 에이전트: 상용화제, 가소제.
- 기능성 첨가물: 산화방지제, 안정제, 착색제.
- 충전제 : CaCO3 옥수수전분 등
빛에 의한 분해를 통해 플라스틱 폐기물을 줄이기 위해 농업용 필름, 포장재, 야외 제품에 사용됩니다.
광분해성 마스터배치:
일반적으로 자외선을 포함한 햇빛에 노출되면 분해를 촉진하는 첨가제를 포함하고 있습니다.
광분해성 마스터배치의 주요 구성 요소는 다음과 같습니다.
- 기본 폴리머: 폴리에틸렌(PE), 폴리프로필렌(PP), 폴리스티렌(PS).
- 광분해성 첨가제: 자외선 흡수제, 광산화제 및 분해촉진제(예: 금속 스테아레이트).
- 블렌딩 에이전트: 균일한 분산과 향상된 가공성을 위한 상용화제 및 가소제.
- 기능성 첨가물: 산화방지제, 안정제, 착색제.
- 충전제 : CaCO3 옥수수전분 등
이러한 소재는 빛에 노출되면 분해가 촉진되어 플라스틱 폐기물을 줄이는 데 사용되는 농업용 필름, 포장재, 실외용 제품과 같은 응용 분야에 사용됩니다.
산화분해성 마스터배치:
열과 산소에 노출되면 플라스틱의 산화와 파편화를 가속화하고, 결국 미세 플라스틱으로 분해되어 미생물에 의해 생분해되는 첨가제를 사용합니다.
산화분해성 마스터배치의 주요 구성 요소는 다음과 같습니다.
- 기본 폴리머: PE, PP, PS.
- 산화분해성 첨가제: 금속 스테아레이트, 전분해성 첨가제.
- 블렌딩 에이전트: 상용화제, 가소제.
- 기능성 첨가물: 산화방지제, 안정제, 착색제.
- 충전제 : CaCO3 옥수수전분 등
플라스틱 폐기물을 줄이기 위해 포장재, 농업용 필름, 일회용 제품에 사용되며, 산화를 촉진하고 생분해를 촉진합니다.
어떤 유형의 분해성 마스터배치를 생산해야 하든, 당사의 압출 및 펠릿화 생산 라인은 효율적이고 고품질의 생산을 달성하는 데 도움을 드릴 수 있습니다.
어떤 유형의 분해성 마스터배치를 생산하든, Granuwel 압출 및 펠릿화 생산 라인이 효율적이고 고품질의 생산을 달성하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
분해성 마스터배치는 어떻게 만들어지나요?
분해성 마스터배치는 아래 그림과 같이, 분해성 마스터배치 압출 및 펠릿화 라인을 통해 제조됩니다.
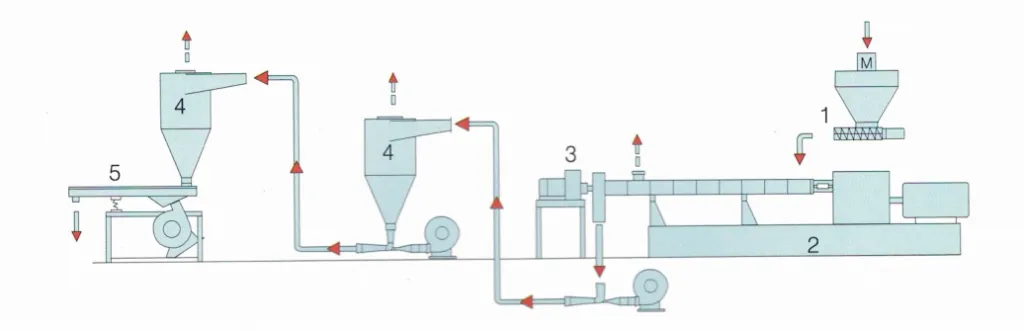
생산에는 원료 선택부터 최종 압출 및 펠렛화 공정까지 여러 가지 핵심 단계가 포함됩니다. 분해성 마스터배치가 어떻게 만들어지는지에 대한 자세한 분석은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 원자재 선정
- 베이스 폴리머: 폴리에틸렌(PE), 폴리프로필렌(PP) 또는 기타 유형의 플라스틱 수지와 같이 일반적으로 사용되는 폴리머입니다.
- 필러 : CACO3분말, 옥수수전분말, 일반적으로 1250메시 이상 크기의 메쉬 사용
- 분해성 첨가제: 여기에는 유기 화합물, 금속 스테아레이트 또는 전분 기반 첨가제와 같이 분해를 촉진하는 물질이 포함됩니다.
- 기타 첨가물: 원하는 특성에 따라 산화방지제, 자외선 안정제, 가소제와 같은 다른 첨가제가 포함될 수 있습니다.
2. 무게 측정 및 혼합
- 정확한 무게 측정: 원료의 무게를 정확하게 측정하여 기본 폴리머와 분해성 첨가제의 올바른 비율을 보장합니다.
- 사전 혼합: 압출 공정에 들어가기 전에 첨가제가 균일하게 분포되도록 재료를 미리 혼합합니다.
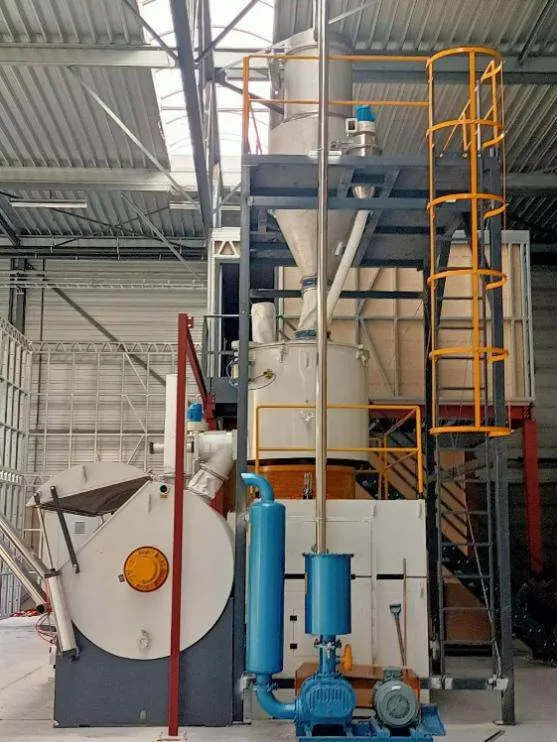

추가 옵션: 감량 계량 공급은 공식 비율에 따라 트윈 스크류 호스트를 자동으로 공급하는 데 사용할 수 있으므로 고속 믹서의 혼합 과정에서 먼지로 인한 환경 오염을 피할 수 있습니다. 또한 근로자의 노동 강도를 줄일 수 있습니다. 그러나 CaCO3 및 옥수수 전분은 코팅된 재료여야 한다는 점에 유의해야 합니다.

3. 압출 공정
- 급송: 미리 혼합된 재료는 공급 시스템(체적식 또는 중량식)을 통해 압출기에 공급됩니다.
- 용융 및 복합화: 압출기 내부에서 재료가 가열되어 기본 폴리머가 녹습니다. 스크류 메커니즘은 폴리머를 분해성 첨가제와 혼합하여 균일한 블렌드를 보장합니다.
- 트윈스크류 압출기: 더 나은 혼합 성능으로 인해 더 복잡한 제형에 선호됩니다.
4. 성형 및 냉각:
- 다이 헤드: 용융된 혼합물을 다이 헤드에 밀어넣어 연속된 가닥으로 만듭니다.
- 냉각: 압출된 스트랜드는 일반적으로 공기 냉각 시스템을 사용하여 냉각되어 재료가 응고됩니다. 공기 냉각 스트립을 사용하고 수냉은 사용하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. 입자가 물에 노출되면 분해되고 1m의 전분 때문에 물을 흡수하기 때문입니다. 그 후 건조해야 합니다.
5. 펠렛화:
절단: 냉각된 스트랜드는 펠렛화기를 사용하여 균일한 펠릿으로 절단됩니다. 다음을 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 스트랜드 펠레타이저: 식은 후 가닥을 자릅니다.
- 수중 펠릿화기: 펠릿 크기를 더 일정하게 유지하기 위해 물속에 있는 동안 가닥을 자릅니다.
6. 건조:
습기 제거: 펠릿을 건조하여 잔류 수분을 제거합니다. 이때 다음과 같은 방법을 사용합니다.
- 원심 건조: 원심력을 이용하여 물을 제거합니다.
- 유동층 건조: 뜨거운 공기를 이용해 펠릿을 건조합니다.
7. 체질 및 분류:
- 균일한 크기: 펠릿을 체질하고 분류하여 크기가 균일하고 크기가 너무 크거나 작은 입자가 없는지 확인합니다.
8. 품질 관리:
생산 과정 전반에 걸쳐 품질 관리 조치가 구현되어 분해성 마스터배치가 필요한 사양 및 성능 표준을 충족하는지 확인합니다. 여기에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- 테스트: 샘플은 일관성, 분해 특성 및 기타 관련 매개변수에 대해 테스트됩니다.
- 조정: 제품 품질을 유지하기 위해 제형이나 공정 조건에 필요한 조정이 이루어집니다.
분해성 마스터배치 사용의 이점
환경 영향: 플라스틱 분해를 가속화하여 장기적인 폐기물 축적을 줄입니다.
비용 효율성: 완전히 생분해성 플라스틱과 비교하여 저렴한 솔루션을 제공합니다.
다재다능함: 포장 및 농업을 포함한 다양한 폴리머 및 응용 분야와 호환 가능합니다.
자원 효율성: 재생 가능한 자원을 활용하고 화석 연료에 대한 의존도를 낮춥니다.
규정 준수: 환경 규정 및 표준을 충족하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
향상된 제품 성능: 유연성, 강도, 자외선 저항성 등의 특성이 향상되었습니다.
브랜드 이미지: 지속 가능성에 대한 신뢰성을 강화하고 환경을 의식하는 소비자에게 어필합니다.
폐기물 관리: 폐기물 처리 및 관리와 관련된 비용을 줄여줍니다.
분해성 폴리머 마스터배치 압출 및 펠릿화에 관한 다른 질문이 있으시면 언제든지 문의해 주십시오. 그라누웰 기계.
